What is iMAPS?
Microbes have thrived on Earth for 3.8 billion years and are the invisible architects of life. They support the health of humans, animals, plants, and ecosystems - yet less than 1% of the natural microbiome has been explored or utilized.

Facing challenges from modernization,antibiotic overuse, climate change, and biodiversity loss, preserving and mobilizing microbial diversity is more urgent than ever. Current methods, focused on community-level sequencing, cannot reveal the living in-situ metabolic functions of microbial cells–the very “dark matter of life."
iMAPS introduces a new paradigm: powered by China's original single-cell Raman instruments, Al-driven analytics, and global
What We Deliver
A global in-situ microbial metabolic atlas across diverse ecosystems.
Open-access or sovereign -governed strain repositories, enriched with complete6W metadata.
Intelligent workflows linking cultivation, sequencing,multi-omics, and reuse.
Demonstrated applications in healthcare,sustainable agriculture, infectious disease control, environmental restoration, and green biomanufacturing
iMAPS Vision
iMAPS Mission
Our Approach

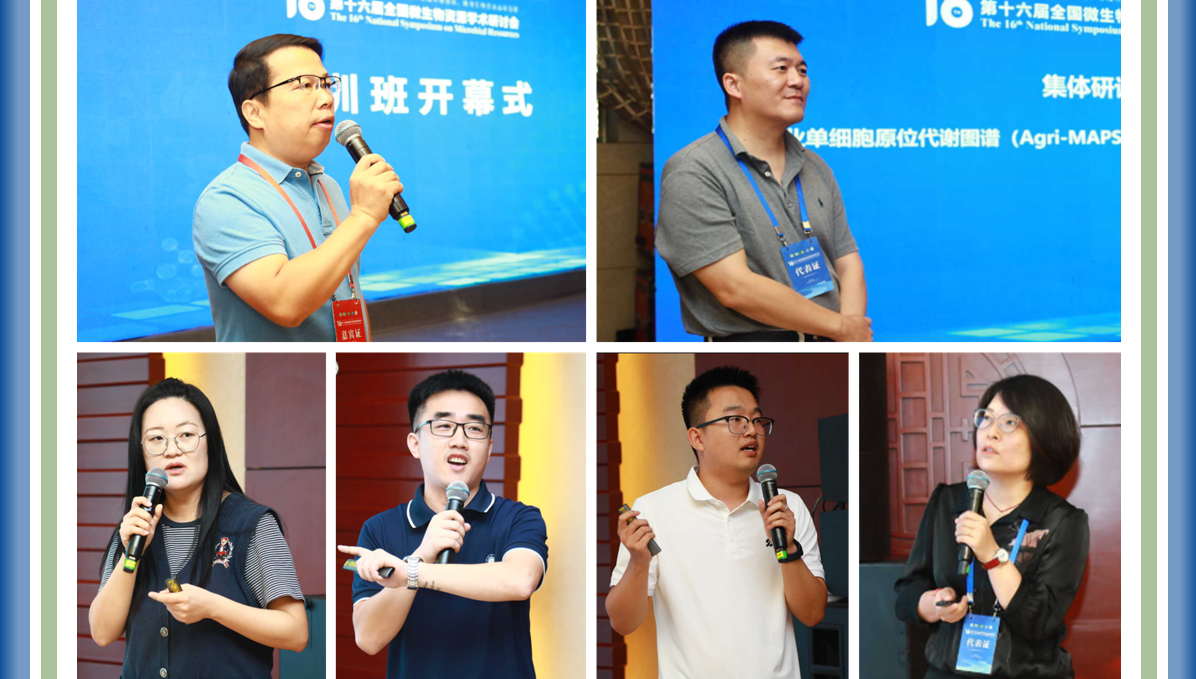
History & Milestones
FAQs
-
The International in-situ Metabolic Atlas Project @ Single-cell — a global effort to explore, preserve, and apply the hidden metabolic power of microbes at single-cell resolution.
-
Unlike traditional metagenomics, iMAPS reveals living metabolic functions directly in single cells, enabling real-time detection, sorting, cultivation, and reuse.
-
An original approach integrating single-cell Raman spectroscopy with isotope probing and multi-omics, offering an exhaustive functional lens on microbial “dark matter.”
-
Academic researchers, industry partners, and policy organizations worldwide are welcome to join the iMAPS network.
-
In precision health, sustainable agriculture, infectious disease prevention, environmental restoration, clean energy, and advanced biomanufacturing.







